Lately, the word "Genetically Modified" has been getting a bad reputation. People do not want the food they eat to be altered in any way. But what people don't see is that farmers need to meet production demand and to do so under a steady budget. Farmers must keep their crops in good shape while factors such as water, fertilizer, bad soil and insects are keeping them from their goal. Farmers use genetically modified crops as a way to improve their crops to keep them alive and increase yield. Some reasons why farmers modify their plants are drought, bad soil, reduced fertilizer, herbicide and harsh environments. Without these modifications, crops would die and people would not get their food. Genetically Modified Crops- What are they? The term GM foods or GMOs (genetically-modified organisms) is most commonly used to refer to crop plants created for human or animal consumption using the latest molecular biology techniques. These plants have been modified in the laboratory to enhance desired traits such as increased resistance to herbicides or improved nutritional content. The enhancement of desired traits has traditionally been undertaken through breeding, but conventional plant breeding methods can be very time consuming and are often not very accurate. Genetic engineering, on the other hand, can create plants with the exact desired trait very rapidly and with great accuracy. Not only can genes be transferred from one plant to another, but genes from non-plant organisms also can be used. (1) How does it work? Genetic engineering techniques now allow scientists to insert specific genes into a plant or animal without having to go through the trial-and-error process of selective breeding. Genetic engineering is therefore extremely rapid compared to selective breeding. With genetic engineering, you can also cross species very easily. (2) |
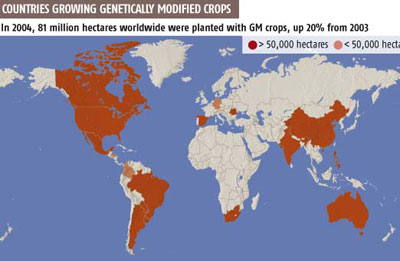 Picture provided by humanflowerproject.com  Picture provided by ourpieceongreenpeace.wordpress.com
Benefits and Concerns
 Here is a picture of genetically modified corn on the right with the drought tolerance gene and normal corn on the left. Provided by monsanto.com |